Cross-Platform vs Native Mobile Development: What’s Right for your Project?
When planning a new mobile application, there are a lot of things to consider, such as development cost, time, and app functionality. Especially if you want to target both Android and iOS audiences.
Mobile app development is a field of continuous, rapid evolution, with new technologies and frameworks emerging annually. This constant influx can make the decision difficult when choosing the optimal strategy for your project: should you opt for a native app development or a cross-platform approach?
This article breaks down the pros and cons of each of them to help you make an informed decision for your project.
Understanding the Two Approaches
Native Development
Native development involves building separate applications specifically for each platform (iOS and Android) using the platform-specific programming languages and tools.
iOS: Swift or Objective-C, using Xcode IDE.
Android: Kotlin or Java, using Android Studio IDE.
Cross-Platform Development
Cross-platform development, also called multiplatform development, uses a single codebase that can be compiled and deployed to both iOS and Android devices. This is achieved using open-source frameworks like React Native, Flutter, and Kotlin Compose.
Some frameworks, such as Flutter, extend beyond mobile application development. They allow developers to reuse the same codebase for various platforms, including web applications, smartwatch apps, and even full-fledged desktop programs.
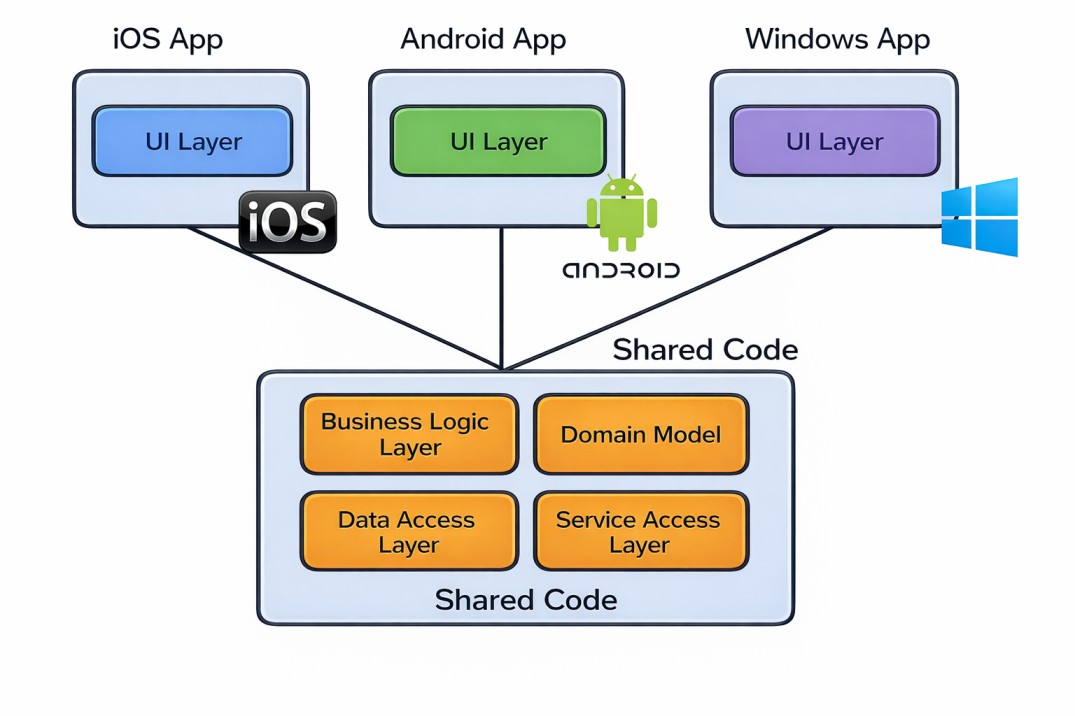
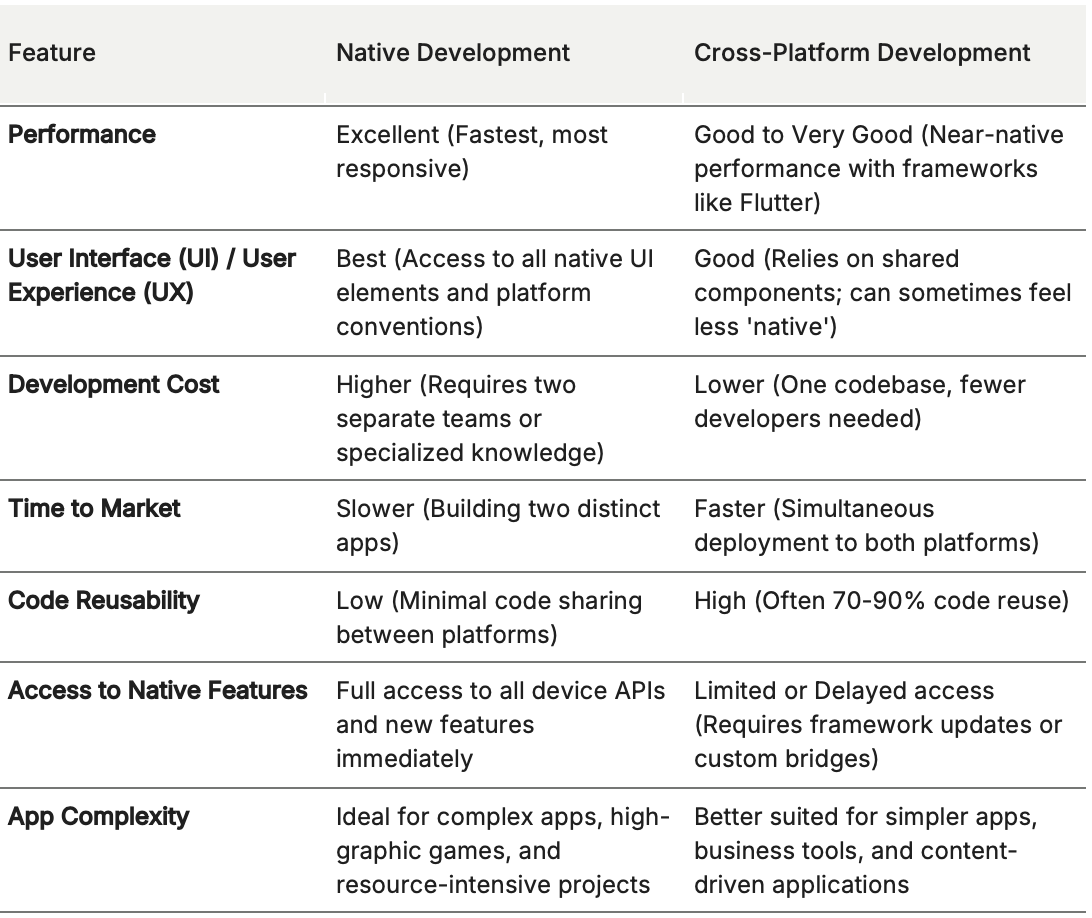
A Comparative Analysis To see how these two approaches stack up, consider the following key factors:
Deeper Dive into Pros and Cons
Native Development
Pros
- Unmatched Performance: Since the code is written in the platform’s native language, it interacts directly with the device’s hardware, resulting in the best possible speed and reliability.
- Best UX: Apps feel seamless, conforming perfectly to the platform’s design guidelines and providing immediate access to the latest UI and UX features.
- Full Hardware Access: Immediate and complete access to all new device features (e.g., specific sensors, AR/VR capabilities).
Cons
- Higher Cost and Time: Essentially building two distinct applications, which doubles development time and cost.
- Maintenance: Requires managing and updating two separate codebases.
Cross-Platform Development
Pros
- Cost Efficiency: Significant cost savings due to a single development team working on one codebase.
- Faster Deployment: Quicker to launch on both iOS and Android simultaneously.
- Simplified Maintenance: Easier to update features and fix bugs across both platforms with a single push.
Cons
- Performance Trade-offs: While modern frameworks have improved, there can sometimes be minor performance bottlenecks compared to native apps.
- Limited Native Access: Accessing specific or new platform APIs often requires implementing ‘bridges’ or waiting for the framework to integrate them, which can add complexity.
- Tooling Dependency: Reliance on the third-party cross-platform framework (e.g., needing to wait for a Flutter update when a new Android version launches).
When to Choose Which Approach
Your choice should align with your business goals and technical requirements.
Choose Native Development if:
- Performance is paramount: Your app is a high-performance game, a complex animation-heavy application, or requires extensive use of device resources (e.g., image editing, intensive computations).
- A hyper-specific UX is required: You need the application to feel 100% compliant with the latest native look and feel of iOS and Android.
- You need bleeding-edge features: Your app relies on the absolute newest hardware or operating system features (e.g., a specific LiDAR sensor feature). Or simply, your app is targeting one specific audience – either Android or iOS.
Choose Cross-Platform Development if:
- Budget and speed are the top concerns: You need to launch quickly on both platforms with a limited budget.
- The app is content-driven: The primary focus is on displaying information, managing user accounts, or handling standard business logic (e.g., e-commerce, social media, utility apps).
- You have a smaller team: A single team can efficiently manage one codebase and deploy it widely. You’re eager to embrace a modern technology that continues to evolve.
Final Thoughts
Both native and cross-platform development offer compelling advantages. If performance, stability, and a deeply integrated user experience are non-negotiable, native is the way to go. However, if speed-to-market, cost efficiency, and broad platform reach are your priorities, modern cross-platform solutions provide an excellent return on investment. We recommend discussing your specific project goals with an experienced development firm to determine the best path forward.
Not sure which approach is right for your app? Reach out to us by email for a tailored consultation based on your technical and business requirements.